

The star system has an apparent magnitude of 1.98. Polaris, designated as Alpha Ursae Minoris, is a triple star system, and currently, it is our North Star or Pole Star, being the closest star to the north celestial pole. In order to view the whole asterism, one needs good viewing conditions and very dark skies since the four stars lying between Polaris, Pherkad, and Kochab, are relatively dim. The distance from the Big Dipper to Polaris is around five times the distance between Merak and Dubhe, the pointer stars. The stars Merak and Dubhe, two bright stars at the end of the Big Dipper’s bowl, point the way to Polaris, and thus the Little Dipper.īy following a line extended from these two stars upwards, out of the celestial bowl, one will find Polaris, the next bright star along the line. The Little Dipper can be found after locating the Big Dipper. Ursa Minor belongs to the Ursa Major family of constellations, along with Coma Berenices, Bootes, Camelopardalis, Canes Venatici, Corona Borealis, Draco, Leo Minor, Lynx, and Ursa Major. The neighboring constellations around Ursa Minor are Camelopardalis, Cepheus, and Draco.

Ursa Minor is located in the third quadrant of the northern hemisphere (NQ3). The constellation has been traditionally important for navigation, particularly by mariners. Ursa Minor spreads out for over 256 square degrees, being easy to spot since it hosts the north pole star. The Little Dipper is situated in the constellation of Ursa Minor, the 56 th largest constellation in the sky. Since in his era, the North Celestial Pole was marked by the stars Kochab and Pherkad, the two stars were given the title of Guardians of the Pole.
Little dipper constellation how to#
Thales created the new constellation after Phoenician sailors had shown him how to use the stars of the Little Dipper to find north. The constellation of Draco is still looping around Ursa Minor in the sky.
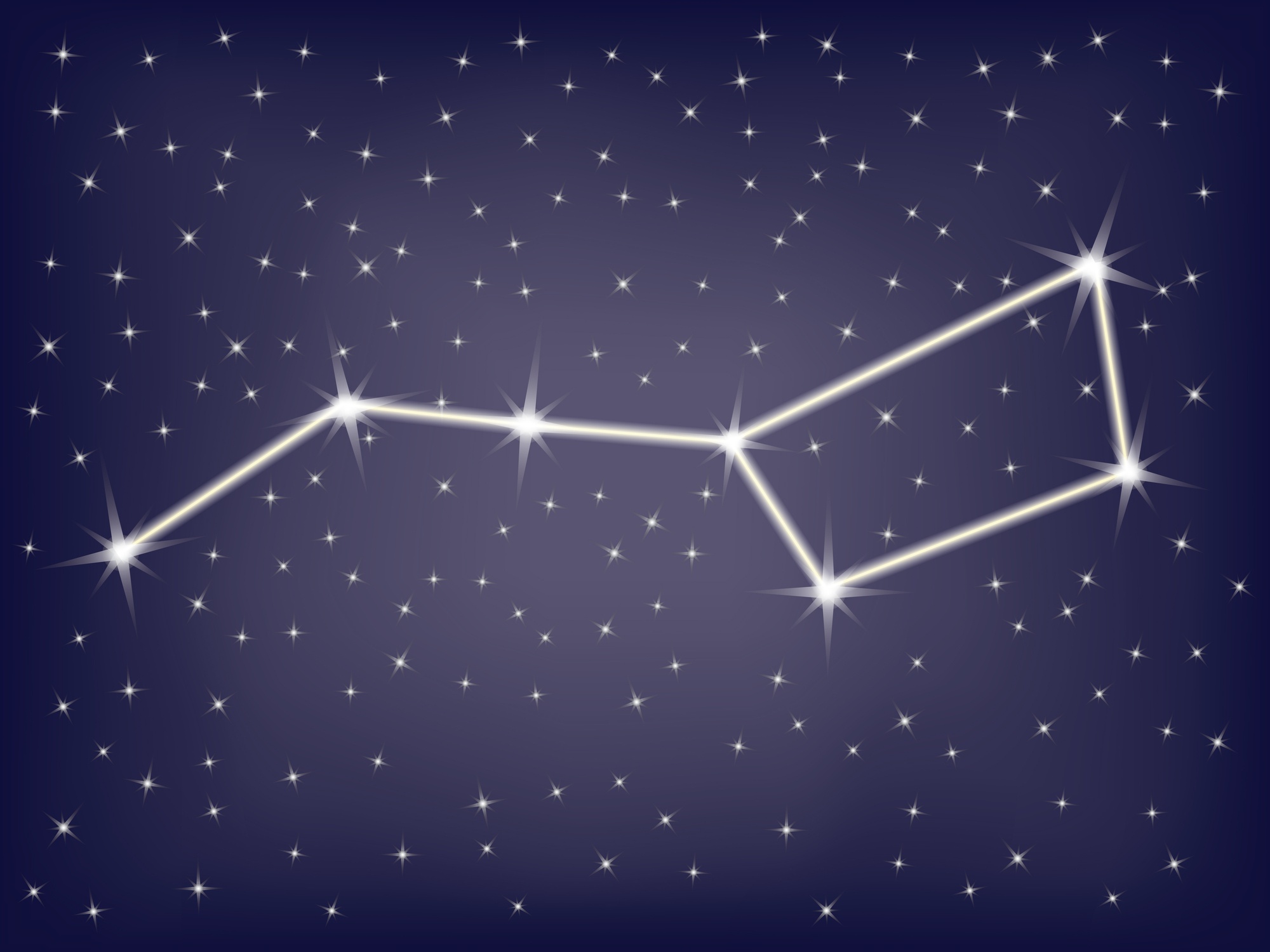
The constellation of Ursa Minor was created by the Greek philosopher and astronomer, Thales of Miletus, around the year 600 BC from the stars that previously marked the wings of Draco, the celestial dragon. In order to view the whole asterism, one needs good viewing conditions and very dark skies since the four stars lying between Polaris, Pherkad, and Kochab, are relatively dim.The best time of the year to observe the Little Dipper is June, at around 21:00 – 9 p.m.To find the North Pole Star – Polaris – one can use the stars Dubhe and Merak – which are part of the Big Dipper asterism – as pointer stars.The Little Dipper asterism can be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the North American name.Kochab, the second-brightest star of Ursa Minor, is a former North Pole Star.This star is very useful to sailors since the star’s angle above the horizon can also be used to find your latitude on Earth.Polaris reveals the location of the North Celestial Pole, being more accurate than any compass.
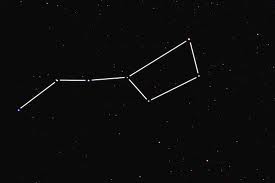
The brightest star of the asterism, Polaris, is currently the North Pole Star, and the brightest star of Ursa Minor.The seven stars that form the Little Dipper asterism are Polaris, Kochab, Yildun, Pherkad, Ahfa al Farkadain, Anwar al Farkadain, and Urodelus.The handle of the Dipper is formed by the stars that mark the celestial Bear’s tail, while the Dipper’s cup is formed by the stars that mark the Beark’s flank.The Little Dipper is formed out of the primary stars of Ursa Minor, however, they are not the only stars in the constellation.The Little Dipper is often confused for the whole constellation of Ursa Minor, just like the Big Dipper is confused with Ursa Major, the Great Bear, however, the Little Dipper is just the brightest part of Ursa Minor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
